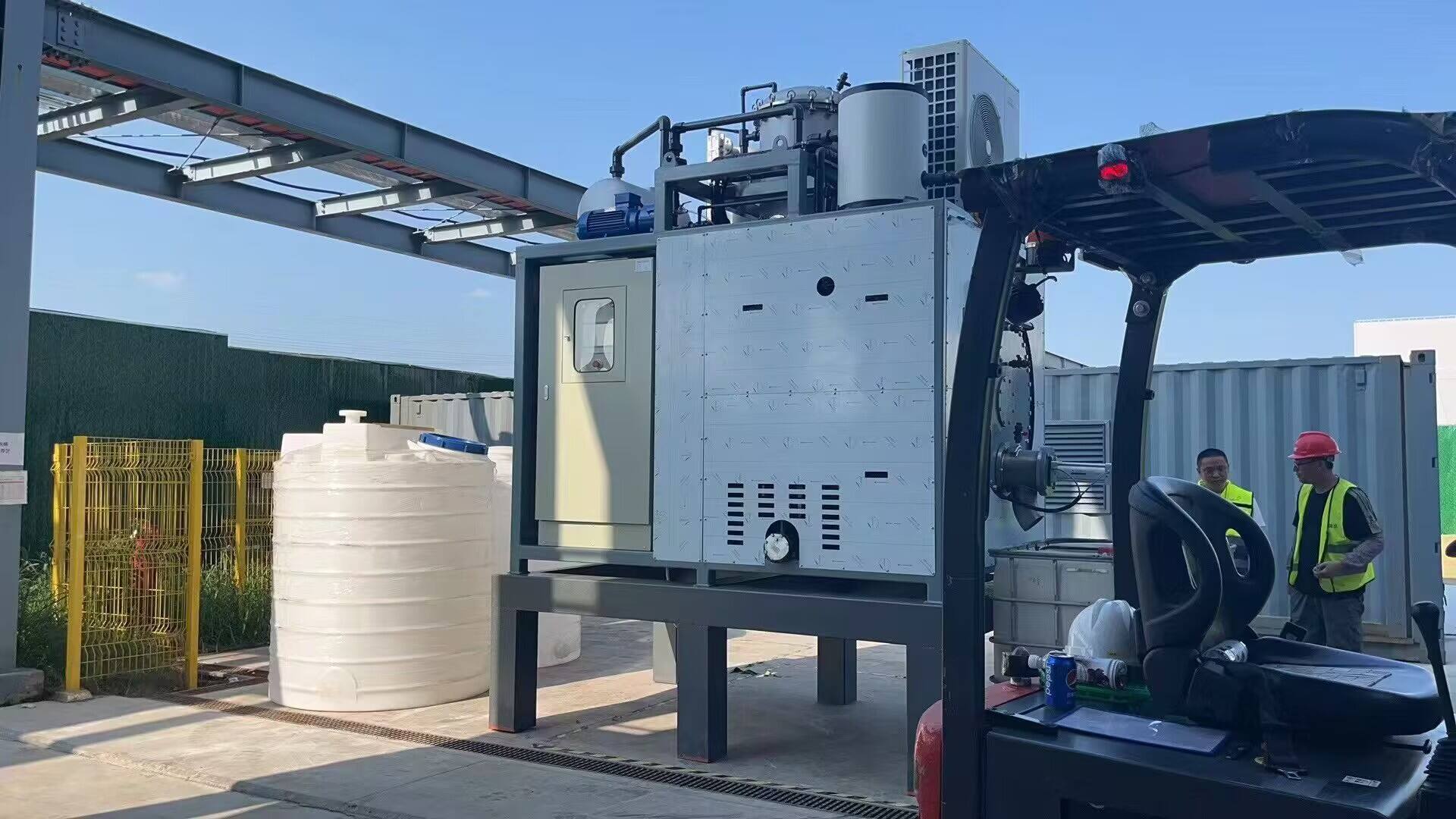
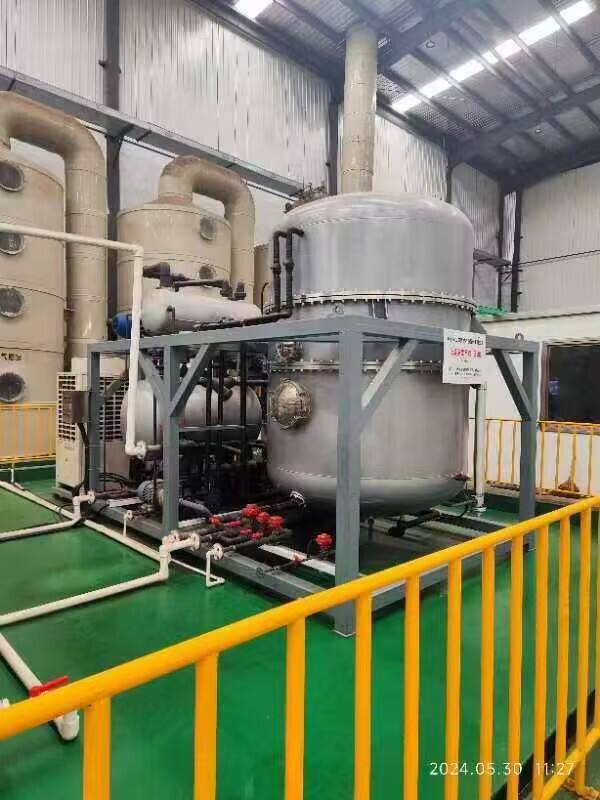
effluent treatment plant in textile industry
An effluent treatment plant (ETP) in the textile industry is a sophisticated system designed to treat and purify wastewater generated during various textile manufacturing processes. The primary function of an ETP is to remove harmful pollutants, chemicals, and contaminants from textile wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. These plants employ a combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods to achieve optimal results. The process typically begins with preliminary treatment, involving screening and equalization, followed by primary treatment that includes sedimentation and flotation. Secondary treatment utilizes biological processes to break down organic compounds, while tertiary treatment focuses on advanced purification methods such as membrane filtration and activated carbon adsorption. Modern ETPs are equipped with automated control systems, real-time monitoring capabilities, and advanced oxidation processes to ensure consistent water quality. They are designed to handle various types of textile effluents, including those containing dyes, heavy metals, suspended solids, and organic pollutants. The implementation of ETPs has become crucial for textile manufacturers to comply with environmental regulations and maintain sustainable operations.